Hotline:400-668-5636

Epoxy due to excellent properties, is not only commonly used as underfill for chips in the semiconductor industry but also widely applied in bonding, sealing, coating, and packaging in fields such as optics, optoelectronics, and medical applications.
Today, we will introduce the characteristics of epoxy resins in optical applications, key points for selection, and application examples.
Types of epoxy resin: 1K or 2K
Epoxy resin is a widely used polymer in high-tech applications, with advantages such as high strength, chemical resistance, good adhesion, and wide temperature tolerance. When selecting, it is crucial to weigh different properties, such as improving flexibility at the expense of some temperature resistance, and the most basic trade-off is choosing between one-component or two-component epoxy resins.
Two-component epoxy resin, commonly known as AB glue, is mixed by volume and can cure at room temperature or when heated. Heating can accelerate the curing process, meeting various production requirements. One-component epoxy resin does not require mixing; it only cures when heated to 250-300°F, allowing for unlimited working time at room temperature. However, due to the sensitivity of many optical components to heat, two-component epoxy resin is more commonly used in optical applications.
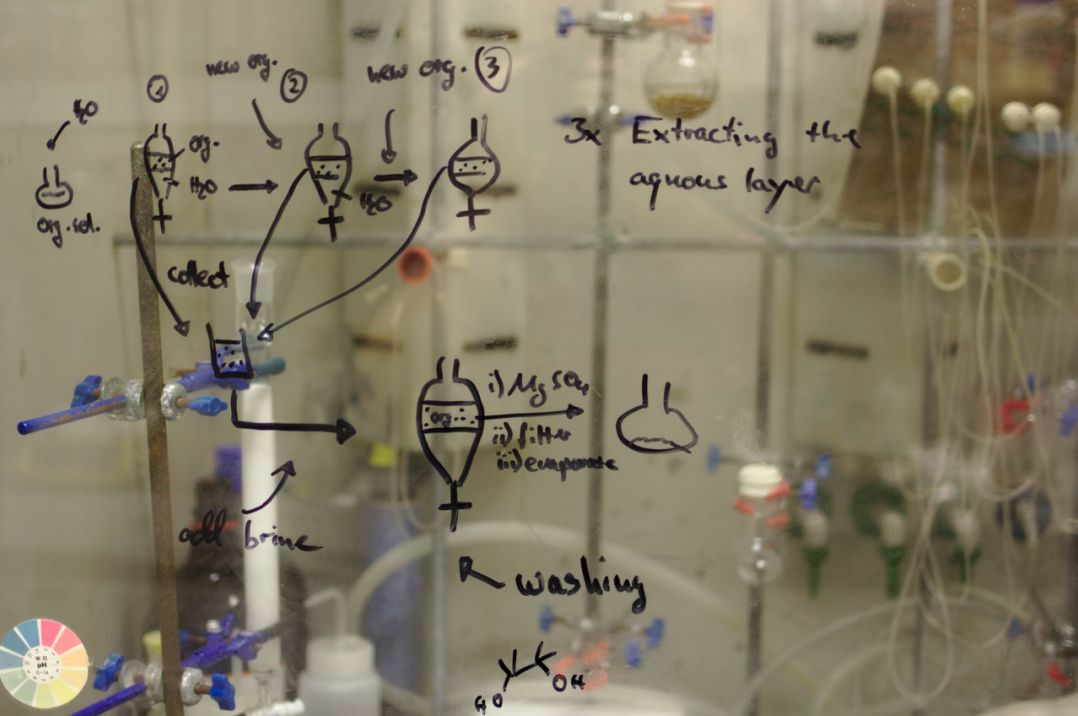

Curing Process of Epoxy
Epoxy resin curing is a polymerization or cross-linking reaction. One-component epoxy resin usually needs 125°C or higher temperature curing, some new models can be cured at 80°C, and must be heated throughout the curing process, stop heating in the middle will end the curing process.
Two-component epoxy resin curing occurs in three stages: open time (the period after mixing when it can be used), working time (the time it takes for the adhesive to solidify and become mobile enough to bond components), and curing time (the duration required for complete curing). Most two-component epoxies cure completely at room temperature, but this process is time-consuming. Heating (50-100°C) can accelerate curing and enhance the performance of the epoxy resin,
Important Features before Curing
1
Before curing, the color, viscosity, and heat release during curing of epoxy resin are important considerations. In terms of color, single-component and two-component epoxy resins vary from transparent to opaque. In optical applications, not all products require optical transparency; for instance, some optoelectronic applications value thermal conductivity, making the opacity of epoxy resin acceptable. When bonding mirrors and metals, there is no need for an optically transparent adhesive.
Viscosity is equally critical, with different applications requiring varying levels of viscosity. Low-viscosity products are needed when entering narrow gaps; adhesive applications may require medium viscosity or paste-like products. Selecting the appropriate viscosity involves a comprehensive consideration of application type, component shape and size, material application method, and post-curing performance requirements, sometimes requiring repeated testing to determine. Additionally, the heat release during the mixing of two-component epoxy resins cannot be overlooked. Systems with low heat release have longer open times and slower curing rates, making them suitable for thicker encapsulations; systems with high heat release have shorter working lives and faster curing rates, making them unsuitable for thick sections. One-component compounds typically have higher heat release, making it difficult to cure parts thicker than ¼ inches, whereas two-component materials can easily cure parts up to one inch and even thicker, making them more suitable for potting applications.
2
Important characteristics after Curing
After curing, the optical properties, electrical properties, chemical resistance, temperature resistance, low outgassing, and hardness of epoxy resins are crucial. In terms of optical properties, the light transmittance at different wavelengths is a key indicator. Most transparent epoxy resins perform well in the range of 350nm to 2.5μm, with significant differences in transmittance above 2.5μm; the refractive index after curing typically ranges from 1.5 to 1.65. Regarding electrical properties, epoxy resins are generally excellent insulators but can also be made conductive. They can be designed to be thermally insulating or both thermally and electrically conductive as required.
In terms of chemical resistance, epoxy resins can withstand the erosion of water, fuel, acids and bases, as well as various solvents. Temperature tolerance is a key reason for their widespread application; some epoxy resins can be used in low-temperature environments, while others can endure temperatures up to 500-600°F. Many also perform excellently in thermal cycling applications. In optical applications, low outgassing is crucial. Several epoxy resins from Elfa New Materials have passed NASAs ASTM C-595 standard, which is typically considered to have low outgassing.
In addition, the hardness of epoxy resin can be adjusted. Rigid epoxy resin is suitable for applications requiring dimensional stability, machining and polishing, while flexible epoxy resin is useful for bonding different substrates in thermal cycling environments.
Applications of Epoxy
1.Semiconductor
In the field of electronics and electrical engineering, epoxy resin is widely used. For example, in chip packaging, epoxy resin serves as a packaging material that protects chips from external environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and chemical substances. Due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, it effectively prevents short circuits between chip leads, ensuring stable operation of electronic devices. Taking the chips on computer motherboards as an example, after being encapsulated with epoxy resin, the reliability and lifespan of the chips are significantly improved, reducing the incidence of failures caused by environmental factors.
2.Aerospace
The aerospace industry has extremely stringent requirements for material performance, and epoxy resins play a crucial role in this field. Carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy matrix composites are one of the ideal materials for aerospace structural components. For example, UAV (U n manned Aerial Vehicles) wings and fuselages are manufactured using these composite materials, which can significantly reduce structural weight while substantially enhancing the strength and stiffness of the components. Compared to traditional metal materials, the use of carbon fiber/epoxy composites has greatly improved aircraft fuel efficiency, reducing operating costs.
3.Robotics
In the field of embodied intelligent robots, motors, as key power output components, directly influence the robots motion performance and task execution capabilities. The application of epoxy resin in various types of motors plays a crucial role in enhancing their overall performance, stability, and lifespan. Different types of motors have distinct characteristics in their selection and usage of epoxy resin due to differences in application scenarios and performance requirements.
Frameless torque motors are often used in the joints of humanoid robots. Epoxy resin is filled with its internal gaps. With the characteristics of low viscosity, high thermal conductivity, low shrinkage, high hardness and good toughness, it reduces bubbles and cavities, conducts heat, ensures dimensional stability, enhances impact resistance, and ensures stable operation of the motor.
The hollow cup motor is used for the dexterous hand. Epoxy resin is coated or filled around the coil to fix the coil and prevent displacement and loosening, while using its insulation to avoid short circuit. Some of them are also used to bond the stator and housing to enhance stability and reduce vibration noise.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor is used in industrial robot manipulators, etc. Epoxy resin impregnated stator windings are formed to form a protective film, enhance insulation and mechanical strength, block external pollutants, and also used to bond magnetic steel to ensure magnetic performance and efficient operation of the motor.
The stepper motor is used for the joint of simple service robot. The internal components are bonded and fixed with epoxy resin to reduce vibration and noise, and the potting improves the protection performance, so that it can adapt to harsh environment.
The brushless DC servo motor is used for medical rehabilitation exoskeleton, epoxy resin is used for insulation treatment and heat dissipation optimization, isolation conductor to prevent short circuit, damping characteristics to reduce noise, high thermal conductivity to help heat dissipation, ensure the long-term stable operation of the motor.
Examples of Epoxy Products
AlphaPro offers a variety of epoxy products suitable for optical applications.
Among the two-component epoxies, EP 401 is a low-viscosity, room-temperature curing adhesive and sealant with a mixing ratio of 2:1. It provides high-strength bonding and excellent dimensional stability, making it popular among customers who use it as thread locking adhesive or for securing components while effectively resisting impact;
EP 399 is highly flexible and optically transparent, with heat cycle resistance, ideal for potting and encapsulation. Many customers apply it to devices like laser projectors and robotic vacuum cleaners that require efficient heat dissipation;
EP 662 is a high-temperature resistant specialty adhesive that bonds well to glass and is acid and alkali resistant, suitable for complex environments;
EP 304 has excellent resistance to yellowing and a long open time, making it suitable for assembling various optical components and photonic displays.
One-component epoxy EP171 is a thermosetting structural adhesive suitable for screen printing, offering long service life and good shear and peel strength.